AMD very recently announced its fourth-generation EPYC™ CPUs.This generation will provide innovative solutions that can satisfy the most demanding performance-intensive computing requirements for cloud computing, AI and highly parallelized data analytic applications. The design decisions AMD made on this processor generation strirke a good balance among specificaitons, including higher CPU power and I/O performance, latency reductions and improvements in overall data throughput. This lets a single CPU socket address an increasingly larger world of complex workloads.
The new AMD EPYC™ 9004 Series processors demonstrate advances in hybrid, multi-die architecture by decoupling core and I/O processes. The new chip dies support 12 DDR5 memory channels, doubling the I/O throughput of previous generations. The new CPUs also increase core counts from 64 cores in the previous EPYC 7003 chips to 96 cores in the new chips using 5-nanometer processes. The new generation of chips also increases the maximum memory capacity from 4TB of DDR4-3200 to 6TB of DDR5-4800 memory.
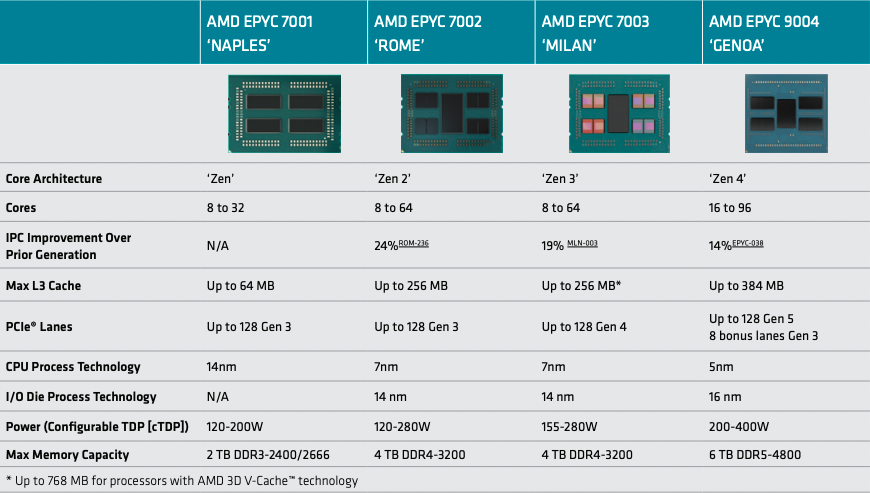
There are three major innovations evident in the AMD EPYC™ 9004 processor series:
- A new hybrid multi-die chip architecture coupled with multi-processor server innovations and a new and more advanced Zen 4 instruction set along with support for an increase in dedicated L2 and shared L3 cache storage
- Security enhancements to AMD’s Infinity Guard
- Advances to system-on-chip designs that extend and enhance AMD Infinity switching fabric technology,
Taken together, the new AMD EPYC™ 9004 series processors can offer plenty of innovation and performance advantage. The new processors offer better performance per watt of power consumed and better per core performance, too.



